FOREX Managed Account Service
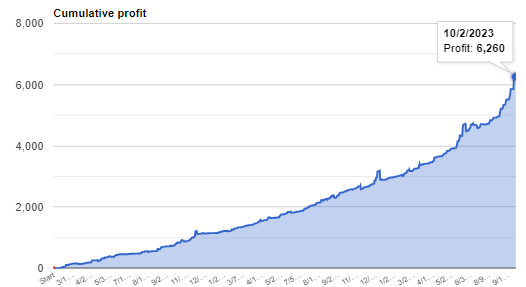
Our Forex Managed Account Service transcends traditional tools to become a comprehensive financial partnership. We pave the way to success by managing your accounts with expert precision and creating a conducive environment for profitable Forex trading. With our service, your financial prosperity is not just possible—it’s assured!
We will do it for you!
Allow us to navigate the intricacies of Forex trading while you enjoy the benefits. Just set up and fund your account, and let our experienced professionals take over. With our meticulously designed platform, robust backup systems, and strategic lot allocation, you’re completely supported. Sit back and witness your investment soar to new heights. Embark on a path to financial freedom with us, where your success is our foremost priority!
Benefits of Opting for Our Managed Forex Accounts Service
Effortless Setup
Professional Account Management
Tailored Lot Sizing
Reliable Returns
24/7 Account Access
Advanced Infrastructure
Comprehensive Educational Resources
Continuous Support
Who Should Consider Our Forex Managed Account Service?
Our Forex Managed Account Service is diverse and crafted to accommodate various types of users, from individuals to institutions. Regardless of your experience level or trading knowledge, our services are adapted to fit your unique requirements. The following groups will find our service particularly advantageous:
Novice Traders
Intermediate Traders
Busy Individuals
Risk-Averse Individuals
Institutions
Experienced Traders
Business Owners
Job Professionals
AI Enthusiasts
Finance Enthusiasts
This service is perfect for anyone looking to enhance their trading effectiveness while managing daily responsibilities or seeking expert guidance in the Forex market.
Our Forex Managed Account Service offers a complete financial solution tailored to accommodate diverse trading requirements and lifestyles. If you belong to any of the following categories, this service is designed to provide you with significant trading benefits.
FAQ
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading or currency trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies on the global foreign exchange market. This market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. The primary objective of forex trading is to earn a profit from the fluctuations in the exchange rates between currencies.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading involves pairs of currencies, such as the EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), which are traded against each other. When trading forex, you speculate on whether the value of one currency will rise or fall against another. For example, if you believe the euro will strengthen against the dollar, you would buy the EUR/USD currency pair. Conversely, if you believe the euro will weaken against the dollar, you would sell the EUR/USD pair.
Key Features of Forex Trading
Leverage: Forex markets are typically traded with leverage, which means traders can control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. This can amplify both gains and losses.
Liquidity: Due to the vast size of the forex market, it is highly liquid. This means that under normal market conditions, trades can be executed quickly and with minimal price slippage.
Market Hours: The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, which allows traders from around the world to trade during local business hours.
Decentralized Market: Unlike stock markets, which have centralized exchanges, forex trading is conducted electronically over-the-counter (OTC), meaning all transactions occur via computer networks between traders globally.
Participants in Forex Trading
Participants range from large financial institutions and multinational corporations to individual retail traders. Central banks also play a crucial role in the forex market as they can influence currency exchange rates through monetary policy, currency intervention, and other measures.
Strategies in Forex Trading
Traders use various strategies based on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and sentiment analysis to make their trading decisions. Technical analysis involves the study of past market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, considers economic indicators, central bank decisions, political events, and other macroeconomic factors that can influence currency values. Sentiment analysis attempts to gauge the market mood to predict directional changes in the market.
Risks and Considerations
While forex trading offers the potential for profit, it comes with significant risk, particularly because of the market's volatility and the use of leverage. Currency values can fluctuate widely due to unforeseen events or changes in market conditions. Therefore, it is crucial for traders to educate themselves thoroughly, use risk management tools like stop-loss orders, and develop a disciplined trading strategy.
Forex trading's complexity and the high degree of risk involved make it essential for prospective traders to have a clear understanding of what they are undertaking before committing capital to the markets.
Forex managed accounts provide an investment avenue where individuals or institutional investors can have their funds traded in the foreign exchange market by a professional trader or money manager. This arrangement allows investors to participate in forex trading without the need to actively manage the trades themselves. Here's a detailed look at how these accounts operate and what makes them unique.
Structure of Forex Managed Accounts
Forex managed accounts are set up in a way that allows the money manager to trade forex on behalf of multiple clients. This is typically done through one of several structures:
MAM (Multi-Account Manager) Accounts: These allow the money manager to execute trades from a master account, with trades then being distributed to client sub-accounts based on an allocation percentage.
PAMM (Percentage Allocation Management Module) Accounts: Similar to MAM, PAMM accounts distribute the trades based on the percentage of each client's equity in the pooled account.
LAMM (Lot Allocation Management Module) Accounts: Trades are allocated to client accounts in fixed lot sizes, but this requires all participating accounts to have similar balance sizes to work effectively.
Role of the Money Manager
The money manager is responsible for making all trading decisions based on the strategy agreed upon with the clients. Money managers are typically experienced traders with a track record of managing significant funds. They use their expertise to try to generate profits for their clients, for which they charge fees. These fees might include:
Performance Fee: A percentage of the profits earned.
Management Fee: A fixed annual percentage charged on the total assets under management.
Advantages of Forex Managed Accounts
Professional Management: Investors benefit from the skills and experience of professional traders who might have access to more sophisticated market analysis tools and strategies.
Time-Saving: Since the trading is handled by professionals, the investor does not need to spend time monitoring markets and managing trades.
Diversification: Managed accounts can serve as a component of a broader investment strategy, providing diversification away from traditional stocks and bonds.
Customization: Some managed accounts offer levels of customization, allowing investors to set specific goals, risk tolerance, and other trading parameters.
Risks and Considerations
Risk of Loss: Like any trading, there is always the risk of losing money, especially in volatile markets like forex.
Manager Dependence: The success of the investment heavily relies on the skills and decision-making of the money manager.
Costs: The fees associated with managed accounts can be higher than those of self-managed trading accounts. Performance and management fees can erode profits.
Lack of Control: Investors in managed accounts have less control over their trades, as all decisions are made by the money manager.
Transparency and Oversight
Reputable forex managed accounts will provide high levels of transparency regarding their trading strategies, risk management measures, and performance history. Investors should have access to regular reports and audits of the account's performance. Furthermore, choosing a managed account that is regulated by a credible financial authority can provide an additional layer of security and peace of mind.
In conclusion, while forex managed accounts can offer the potential for significant returns through professional trading, they also come with risks that should be carefully considered. Investors looking to invest in these accounts should thoroughly evaluate the credentials of the money manager, understand the fee structure, and consider how these investments fit into their broader financial goals and risk tolerance.
Forex managed accounts offer several compelling benefits for investors, ranging from accessing professional trading strategies to saving time on daily trading operations. These accounts are particularly appealing to those who want to participate in the forex market without committing the time and resources required to develop and implement trading strategies themselves. Here’s a detailed exploration of the primary benefits:
1. Access to Professional Trading Strategies
One of the main advantages of using a Forex managed account is the access it provides to professional trading strategies. Money managers or professional traders who handle these accounts often have a wealth of experience, advanced analytical skills, and access to sophisticated tools and data. They might employ a variety of strategies involving technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both to optimize trading outcomes.
2. Time Savings
Forex trading requires constant market analysis, staying updated with global economic news, and the ability to react quickly to market changes — tasks that are time-consuming and can be overwhelming for most investors. Managed accounts are beneficial as they free up time for investors; the money manager handles all trading activities, monitoring, and decision-making processes involved in managing the trades. This makes managed accounts ideal for those who want exposure to forex markets but do not have the time to manage trades actively.
3. Diversification of Investments
Forex managed accounts allow investors to diversify their investment portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Currency trading involves different factors and dynamics compared to other asset classes, providing an alternative avenue for capital allocation. This diversification can potentially reduce risk as the performance of forex investments is generally not correlated with most other asset classes.
4. Risk Management
Professional money managers often have better risk management techniques and tools at their disposal. They can employ various strategies such as diversifying across different currency pairs, using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and appropriately leveraging positions to manage exposure. Having a managed account means benefiting from such professional risk management, which might be harder to achieve for individual traders without similar resources.
5. Potential for Customization
Depending on the account setup and the brokerage or money management service used, investors might be able to customize their investment according to their specific risk tolerance, investment goals, and other personal preferences. For instance, some services might allow investors to set specific guidelines regarding maximum drawdown limits, leverage, or even the currency pairs traded.
6. Regulatory Oversight and Transparency
Reputable managed forex accounts operate under the jurisdiction of financial regulatory authorities and are required to follow strict compliance measures. This setup provides a level of security and transparency in operations. Investors typically receive regular and detailed reports on account performance, trades executed, and strategic adjustments, ensuring visibility into how their investments are being managed.
7. Leverage Expertise
Finally, forex managed accounts leverage the expertise of seasoned professionals who might have insights and market acumen developed over years of trading. This expertise is invaluable, especially in navigating the complex and volatile forex market, where professional analysis and experienced decision-making can significantly impact outcomes.
In conclusion, forex managed accounts offer a convenient and potentially effective way for investors to engage in forex trading. They provide several strategic advantages, including professional management, time savings, diversification, and robust risk management, making them an attractive option for investors looking to expand their financial portfolio into currencies without taking on the day-to-day challenges of trading.
managed account is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of several critical factors. This decision not only involves evaluating the potential financial returns but also understanding the risks and the operational standards of the account. Here are key considerations to take into account before committing to a Forex managed account:
1. Track Record of the Money Manager
The performance history of the money manager is one of the most crucial aspects to consider. A strong, consistent track record over a significant period can be a good indicator of the manager’s skill and reliability. Look for:
Historical performance data that shows not just the returns but also the volatility and maximum drawdowns experienced by the account.
Duration of track record: Longer histories can demonstrate a manager's ability to navigate different market conditions.
Comparison with benchmarks and peers: See how the manager performs compared to similar accounts or market benchmarks.
2. Safety Protocols of the Brokerage
The security of your investment should be paramount. Ensure that the brokerage managing the Forex account adheres to high safety standards:
Security measures for protecting client funds, such as segregation of client funds from company funds, which ensures that client money is not used for operational purposes.
Financial health of the brokerage: Strong capitalization and sound financial practices reduce the risk of the brokerage failing.
3. Regulatory Compliance of the Platform
The regulatory framework within which the managed account operates can greatly
affect the security and integrity of your investment:
Regulatory body: Look for accounts managed by brokerages regulated in reputable jurisdictions (e.g., the U.S. CFTC, UK FCA, Australia ASIC).
Compliance records: Check for any past violations or disciplinary actions against the brokerage or money manager, which could indicate potential red flags.
4. Transparency of Account Operations
Transparency is key in managed accounts, as it provides clarity on how your investment is being handled:
Access to real-time information: Ensure you can monitor the account’s performance and transactions as they happen.
Regular reporting: The account should provide regular and detailed statements and performance reports.
Communication: Assess the ease and openness of communication with the manager. You should feel comfortable with how and when you can discuss your investment.
5. Fee Structure
Understanding how and what you will be charged is crucial:
Performance fees: These are typically a percentage of the profits earned and can vary widely.
Management fees: Some accounts also charge a management fee, which is a percentage of the assets under management (AUM), regardless of performance.
Other costs: Consider additional costs such as entry fees, exit fees, and administrative charges.
6. Investment Strategy and Suitability
The investment strategy should align with your own risk tolerance and investment goals:
Strategy specifics: Understand the types of strategies used (e.g., scalping, swing trading, use of derivatives).
Risk management: Assess how risks are managed, including the use of leverage and safeguards against market volatility.
7. Exit Conditions
Know the terms for withdrawing from the account:
Lock-up periods: Some accounts may have a lock-up period during which you cannot withdraw your funds.
Withdrawal terms and penalties: Understand any fees or penalties for early withdrawal, and how quickly funds can be accessed.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make a more informed decision about whether a Forex managed account is suitable for your investment needs and risk tolerance. This thorough due diligence will help ensure that you entrust your capital to a reliable, competent, and well-regulated money manager.
The safety of Forex managed accounts can indeed vary significantly, largely influenced by the regulatory environment in which the broker operates and the transparency and integrity of their management practices. While investing in Forex through managed accounts can provide substantial returns, it is not without risks. Here are some key factors that influence the safety of Forex managed accounts:
1. Regulatory Oversight
Regulation is perhaps the most critical factor in assessing the safety of a Forex managed account. Brokers regulated in jurisdictions with strict financial regulatory standards are generally safer due to higher compliance requirements. These regulations ensure that:
Broker practices are regularly audited.
Client funds are held in segregated accounts separate from the broker’s operating funds, protecting them in the event that the broker becomes insolvent.
There are compensation schemes in place that may cover investor losses in the case of the broker's failure.
Notable regulatory bodies include the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), the UK's Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
2. Transparency of Account Management
Transparency in how the account is managed also plays a critical role in its safety. A transparent managed account will provide:
Regular, detailed reports on account performance, including profits, losses, fees charged, and the strategies employed.
Real-time access to account activity, allowing investors to monitor the manager’s decisions and the account’s performance actively.
Clear communication regarding any changes in investment strategy or significant trades.
3. Broker's Reputation and Financial Health
The reputation and financial stability of the broker managing the Forex account are also vital:
Long-standing reputation: A broker with a long track record of reliability and good service is likely safer.
Financial stability: A financially sound broker is less likely to face solvency issues that could impact client investments.
4. Risk Management Practices
How risks are managed within the Forex managed account also impacts its safety:
Leverage use: Excessive leverage can amplify losses, especially in volatile markets.
Stop-loss settings: These can protect against large-scale losses by automatically closing out losing positions at a set price.
5. Due Diligence by the Investor
Finally, the diligence exercised by investors themselves can influence the safety of their investment:
Researching and choosing the right broker: Investors should undertake thorough research to ensure the broker and money manager have a good track record and robust safety measures.
Understanding the terms and conditions: Being aware of all terms, fees, and conditions associated with the managed account is crucial.
While a well-regulated and transparently managed Forex account can offer a relatively safe investment opportunity, no investment is entirely risk-free, especially in the volatile Forex market. Investors should always consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when deciding whether a Forex managed account is a suitable investment vehicle for them.
Forex managed accounts employ a variety of trading strategies, each with distinct characteristics and risk profiles. These strategies are chosen based on their potential to achieve the investment goals and manage the risks in line with the preferences of the investors. Here’s a deeper look into some of the common strategies used in Forex managed accounts:
1. Swing Trading
Swing trading is a strategy that involves holding positions for several days to capitalize on expected upward or downward moves in the market. Swing traders utilize technical analysis to identify buying and selling opportunities at the beginning or end of a price swing. This strategy is less time-intensive than day trading but requires a keen understanding of market patterns and the ability to interpret potentially impactful economic events.
2. Scalping
Scalping is a strategy aimed at making profits from very small price changes. Scalpers aim to enter and exit trades quickly, often within minutes or even seconds, to capture quick gains. It involves a high volume of trades and requires a deep understanding of market movements and a highly disciplined approach. Because the profit margin per trade is small, scalpers usually engage in high leverage, which increases the risk.
3. Technical Analysis Strategies
Technical analysis involves studying historical price action and trading volumes to forecast future market behavior. This category includes a variety of techniques and tools, such as:
Chart patterns analysis: Identifying patterns like head and shoulders, flags, and triangles that suggest future price movements.
Technical indicators: Using tools like moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), MACD, and Fibonacci retracements to identify trends, reversals, and potential entry and exit points.
Candlestick patterns: Analyzing candlestick formations to make inferences about market sentiment and potential price movements.
Traders using technical analysis believe that all necessary information about a currency pair can be found in its price chart, making it a popular approach in Forex trading.
4. Fundamental Analysis-Driven Trades
Fundamental analysis in Forex involves evaluating the economic and political conditions that may affect currency prices. This includes analysis of:
Economic indicators: Data such as GDP growth rates, employment figures, inflation, and manufacturing output can influence exchange rates.
Monetary policies: Decisions by central banks on interest rates and quantitative easing impact currency strength.
Political stability and performance: Political events like elections, policy changes, and international relations can cause significant market movements.
Traders using fundamental analysis aim to predict currency movements by interpreting economic conditions and political events, making it suitable for longer-term trades based on more sustained trends.
5. Risk Management Techniques
Regardless of the specific trading strategy employed, risk management remains a crucial component of any Forex managed account strategy. Effective risk management might include:
Setting stop-loss orders: To limit potential losses on each trade.
Position sizing: Adjusting the size of trades based on the volatility of the market and the overall risk profile of the portfolio.
Diversification: Trading multiple currency pairs or combining Forex trading with other asset classes to spread risk.
Each trading strategy has its merits and risks, and the choice of strategy should align with the overall risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals of the investor. Professional money managers tailor these strategies to fit the needs and expectations of their clients, balancing potential returns against acceptable levels of risk.
Fees in Forex managed accounts are a crucial consideration for investors, as they can significantly impact the net returns from their investments. Understanding how these fees are structured will help investors make informed decisions and set realistic expectations about potential returns. Here’s a detailed look at the common types of fees associated with Forex managed accounts and how they typically work:
1. Performance Fees
Performance fees are charged based on the profits generated by the managed account. This type of fee aligns the interests of the money manager with those of the client, as the manager only earns a significant fee if the account performs well. The fee is typically calculated as a percentage of the profits earned.
High Water Mark: This principle is often applied in the calculation of performance fees. It ensures that performance fees are paid only on net new profits. This means that if the account suffers losses and then recovers those losses, the manager will not earn a performance fee on the recovery if the account value is still below the highest level previously achieved.
2. Management Fees
Management fees are charged for the ongoing operation and administration of the managed account. Unlike performance fees, which are dependent on the account making a profit, management fees are typically charged regardless of performance. These fees are usually calculated as a percentage of the assets under management (AUM) and are billed monthly or annually.
Flat Fees: In some cases, especially with smaller accounts, brokers might charge a flat annual or monthly fee instead of a percentage-based fee.
3. Other Potential Fees
Apart from performance and management fees, there may be other costs associated with managing a Forex account:
Entry/Setup Fees: Some managed accounts might charge an initial fee when an investor opens an account. This fee goes towards the cost of setting up the account and allocating resources.
Exit/Redemption Fees: If an investor decides to withdraw funds from the account, some managers might charge an exit fee, especially if the withdrawal occurs within a short period after the account’s inception.
Brokerage Fees: These are fees associated with executing trades within the account, including spreads and any commission costs. While these are not directly billed by the manager, they are costs that investors should be aware of as they affect the overall profitability of trading activities.
4. Fee Transparency and Comparison
It's essential for investors to understand and review all potential fees associated with a Forex managed account before committing their funds. Fee transparency is critical, and prospective investors should expect:
Clear documentation of all fees in the service agreement.
Disclosures about how fees are calculated, when they are charged, and under what circumstances additional fees might apply.
Comparisons with other managed accounts to ensure competitiveness and fairness of the fee structure.
5. Consideration of Fee Impact on Returns
Investors should calculate the potential impact of fees on their investment returns. High fees can significantly eat into profits, especially in volatile markets where profits might already be marginal. Therefore, understanding the fee structure and how it applies under different market conditions is vital for setting realistic expectations about the potential returns from a Forex managed account.
By thoroughly understanding and carefully reviewing the fee structures, investors can better manage their investment choices and align them with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
The minimum investment required for a Forex managed account can vary significantly based on several factors, including the specific provider, the account type, and the strategic objectives of the fund. Understanding these variations is crucial for investors when considering entering the Forex market through a managed account. Here's a closer look at the factors influencing the minimum investment requirements and what potential investors might expect:
1. Provider and Account Type
Different managed account providers and brokers have different thresholds for minimum investments, largely due to the differing cost structures and targeted investor bases:
Retail Investor Accounts: Some providers cater to retail investors and may offer lower minimum investment requirements to make Forex trading more accessible. These minimums can range from a few thousand dollars to $10,000 or more.
Institutional Accounts: For accounts targeted at institutional investors or high net worth individuals, the minimum investment can be significantly higher, often starting at $100,000 or more. These accounts typically offer more sophisticated trading strategies and higher levels of personal service.
2. Strategy Complexity
The complexity and nature of the trading strategy also play a role in determining the minimum investment:
Advanced Strategies: Some complex strategies, such as those involving high-frequency trading or significant diversification across multiple currency pairs, might require higher minimum investments due to the increased management and technology resources needed.
Simpler Strategies: More straightforward strategies might allow for lower minimum investments, making them more accessible to a broader range of investors.
3. Risk Management
The level of risk associated with the managed account’s strategy can also influence the minimum required investment. Managers may set higher minimums to ensure that there is enough capital in the account to effectively implement risk management practices, such as diversification and hedging.
4. Regulatory and Operational Costs
Regulatory compliance and operational costs can impact the minimum investment level. Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and covering operational expenses, such as technology infrastructure, research, and staff salaries, can necessitate a higher minimum investment.
5. Access to Professional Management
The opportunity to have one’s capital managed by professional traders and money managers often justifies the minimum investment threshold. These professionals bring experience and expertise to the table, which can significantly enhance the potential for profitable trading outcomes.
General Recommendations for Investors:
Research: Potential investors should thoroughly research different managed account providers to compare minimum investment requirements.
Understand Terms and Conditions: Be fully aware of all terms, conditions, and any potential additional costs associated with the managed account.
Align with Investment Goals: Ensure that the minimum investment requirement aligns with your overall investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial capacity.
In conclusion, while the minimum investment for Forex managed accounts can vary widely, it fundamentally reflects the provider's strategic approach, the complexity of the trading strategies employed, and the targeted investor demographic. Potential investors should carefully consider these factors in light of their personal investment goals and financial situation.
Monitoring the performance of a Forex managed account is essential for investors to ensure that their investment aligns with their expectations and financial goals. Fortunately, modern technology and financial regulations have made it easier and more transparent for investors to keep track of their accounts. Here’s a detailed look at how investors can effectively monitor their Forex managed account:
1. Online Trading Platforms
Most brokers and money managers provide access to sophisticated online trading platforms that allow for real-time monitoring of account performance. These platforms typically offer:
Dashboard Views: A comprehensive overview of the account’s current status, including the balance, equity, and margin levels.
Detailed Reporting: Access to detailed reports showing historical performance, including profits and losses, trading volumes, and account balance over time.
Open and Closed Trades: Information on all trading activity, allowing investors to see which trades are open and which have been closed, along with the profits or losses from each trade.
2. Mobile Apps
Many brokers also offer mobile applications that provide the same functionalities as their desktop or web counterparts but with the convenience of mobile access. This means investors can check their accounts on the go, anytime and anywhere, which is particularly useful in the fast-moving Forex market.
3. Regular Statements
Brokers typically send out regular statements (monthly or quarterly) that summarize account activity. These statements provide a snapshot of the account’s performance over the statement period, including:
Account Summary: Starting and ending balance, total deposits and withdrawals.
Performance Metrics: Profit or loss during the period, performance against benchmarks if applicable.
Fees and Charges: Detailed listing of any fees or charges deducted from the account, such as management fees or performance fees.
4. Direct Communication
Regular communication with the money manager or the broker’s support team can also provide insights into the account’s performance and any significant trading decisions or market events affecting the account. Many managed account providers schedule regular review meetings (either virtual or in person) to discuss the account’s performance and any necessary adjustments to the trading strategy.
5. Automated Alerts
Setting up automated alerts is another way to stay informed about significant movements or changes in the account. These alerts can be customized according to specific criteria set by the investor, such as performance thresholds, risk levels, or margin calls.
6. Audit Trails
For additional transparency, some managed account platforms provide an audit trail feature that records all actions taken in the account. This can include trade execution, order modifications, and logins. This feature is particularly valuable for ensuring that all account activities are transparent and traceable.
7. Compliance and Regulatory Reports
In regulated markets, brokers are required to adhere to strict reporting guidelines which ensure that they provide accurate and timely information to investors. Keeping an eye on these compliance and regulatory reports can give investors an added layer of assurance about the legitimacy and performance of their managed account.
In summary, effectively monitoring a Forex managed account involves utilizing a combination of real-time data access through online platforms, regular financial statements, direct communications, and leveraging technology like mobile apps and automated alerts. By staying informed and actively engaged with their investment, investors can better manage their expectations and respond promptly to any changes in their account’s performance.
Blogs
Unlock your financial potential today with our Forex Managed Account Service - where your success is our mission.
Why is it important to choose a regulated broker?
The leading platforms for professionally managed accounts are MetaTrader’s MAM (Multi-Account Manager) and PAMM (Percentage Allocation Management Module) technologies. MAM accounts enable a single master account to manage multiple sub-accounts, with trades executed on the master account automatically replicated in the sub-accounts.
Brokers might offer various trade asset allocation methods, with one of the most prevalent being percentage allocation via PAMM technology. This method allocates trades across sub-accounts based on the percentage of funds each investor holds. Another approach, used in LAMM (Lot Allocation Management Module) accounts, distributes trades by lot size, but this method requires all investors to have equal account balances.
Investors typically need to sign a Limited Trading Authorization (LTA) to enable a money manager to trade on their behalf using MAM accounts, though this authorization does not cover deposits and withdrawals.
Copy trading is another popular managed account option. While some brokers utilize MetaTrader for copy trading, others offer proprietary platforms that allow clients to act as strategy providers, earning from their followers’ profits, or to follow others’ trades simply.
For those new to trading, copy trading platforms are often more accessible, not requiring money managers to be licensed or regulated, and enabling clients to start trading with just a few clicks.
For a more professional setup, a MAM account may be appropriate, although it might require the money manager to be licensed, particularly in certain jurisdictions.
For more detailed information, you might want to look into guides on the best MT4 brokers and best MT5 brokers, which can provide further insights into choosing the right platform for managed accounts.
What is the best type of forex brokerage account for managed accounts?
When exploring brokers that offer managed accounts, it’s crucial to evaluate the various account types they provide, along with their respective execution models. Brokers typically present a range of accounts that differ in terms of fees, minimum deposits, and service levels. Generally, accounts requiring higher minimum deposits tend to include more services and lower fees, but it’s essential to assess what best fits your specific needs. This includes examining platforms that facilitate managed account or copy trading services, which may have different terms.
For instance, the minimum deposit for the DupliTrade copy trading platform is $2,000, whereas brokers using MetaTrader may allow deposits as low as $50. However, money managers often require a significantly higher minimum investment.
It is important to conduct thorough research and directly engage with brokers to address any queries. Another critical aspect to consider is the broker’s execution model, especially since managed accounts require quick execution to simultaneously trade across multiple sub-accounts with minimal broker interference.
Typical execution models include:
Market Maker Dealing Desk Accounts: In this model, the broker may take the opposite side of your trades. While some brokers are transparent about this practice, others are not. These accounts might offer fixed spreads, aiming to profit from the difference between the actual market spread and the spread offered to traders.
No Dealing Desk Accounts: These accounts automate order matching with other market participants using algorithms. They come in several forms:
STP Accounts: Straight through processing accounts send client trades directly to the broker’s liquidity providers.
ECN Accounts: Electronic communications network accounts match trades among various liquidity sources like banks and hedge funds in an anonymous network.
DMA Accounts: Direct market access accounts allow traders to engage directly with
other interbank market participants.
Demo Accounts: These accounts provide a risk-free, virtual trading environment, which is excellent for evaluating a broker’s products and services.
Before making a decision, be sure to explore comprehensive guides like “Best Copy and Social Trading Platforms,” “Best STP Forex Accounts,” “Best ECN Forex Accounts,” and “Best Forex Demo Accounts” to find the most suitable option for your trading needs.
How to determine the best leverage for your managed account?
When using a managed forex account, determining the appropriate leverage is crucial, as leverage amplifies both the potential gains and losses from trading. Leverage in forex trading enables traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of deposited funds, essentially borrowing capital from the broker.
For example, with 30:1 leverage, a trader can open a position worth $30,000 using only $1,000 of their own capital. While this can significantly increase potential profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses, particularly if the market moves against the trader’s position.
It’s important to note that leverage involves costs, such as the swap fee or overnight financing fee, which is akin to paying interest on the borrowed amount—similar to a mortgage.
Regulatory changes like the MiFID II regulations introduced in 2018 have led many tier-1 regulated brokers, such as those overseen by the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority), CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission), and ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission), to limit leverage for retail traders to 30:1. This measure is intended to enhance trading safety.
While some brokers, particularly unregulated offshore ones, may offer leverage as high as 1000:1, these providers often lack regulatory oversight and protection, posing a significant risk.
For those managing or following a managed account, it’s crucial to ensure that the account type and leverage settings are consistent across all participating traders. Disparities in account settings can lead to different trading opportunities and outcomes, potentially affecting overall performance and returns.
When using a managed forex account, determining the appropriate leverage is crucial, as leverage amplifies both the potential gains and losses from trading. Leverage in forex trading enables traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of deposited funds, essentially borrowing capital from the broker.
For example, with 30:1 leverage, a trader can open a position worth $30,000 using only $1,000 of their own capital. While this can significantly increase potential profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses, particularly if the market moves against the trader’s position.
It’s important to note that leverage involves costs, such as the swap fee or overnight financing fee, which is akin to paying interest on the borrowed amount—similar to a mortgage.
Regulatory changes like the MiFID II regulations introduced in 2018 have led many tier-1 regulated brokers, such as those overseen by the FCA (Financial Conduct Authority), CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission), and ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission), to limit leverage for retail traders to 30:1. This measure is intended to enhance trading safety.
While some brokers, particularly unregulated offshore ones, may offer leverage as high as 1000:1, these providers often lack regulatory oversight and protection, posing a significant risk.
For those managing or following a managed account, it’s crucial to ensure that the account type and leverage settings are consistent across all participating traders. Disparities in account settings can lead to different trading opportunities and outcomes, potentially affecting overall performance and returns.
Which trading platform is best for managed accounts?
The leading platforms for professionally managed accounts are MetaTrader’s MAM (Multi-Account Manager) and PAMM (Percentage Allocation Management Module) technologies. MAM accounts enable a single master account to manage multiple sub-accounts, with trades executed on the master account automatically replicated in the sub-accounts.
Brokers might offer various trade asset allocation methods, with one of the most prevalent being percentage allocation via PAMM technology. This method allocates trades across sub-accounts based on the percentage of funds each investor holds. Another approach, used in LAMM (Lot Allocation Management Module) accounts, distributes trades by lot size, but this method requires all investors to have equal account balances.
Investors typically need to sign a Limited Trading Authorization (LTA) to enable a money manager to trade on their behalf using MAM accounts, though this authorization does not cover deposits and withdrawals.
Copy trading is another popular managed account option. While some brokers utilize MetaTrader for copy trading, others offer proprietary platforms that allow clients to act as strategy providers, earning from their followers’ profits, or to follow others’ trades simply.
For those new to trading, copy trading platforms are often more accessible, not requiring money managers to be licensed or regulated, and enabling clients to start trading with just a few clicks.
For a more professional setup, a MAM account may be appropriate, although it might require the money manager to be licensed, particularly in certain jurisdictions.
For more detailed information, you might want to look into guides on the best MT4 brokers and best MT5 brokers, which can provide further insights into choosing the right platform for managed accounts.
What to avoid when choosing a managed account?
When selecting a managed account, it’s crucial to verify that the broker possesses the necessary technology to effectively manage client funds. For money managers, it’s essential that trades made on a master account are consistently and accurately executed across all sub-accounts.
From my experience in managing client capital, another critical aspect is the safety and security of the broker. Investors need assurance that their funds are with a reputable broker and that their capital is protected. Therefore, it’s important to choose a broker that is highly regulated by a well-established financial authority.
Additionally, if you are considering following a managed account provider, ensure that the platform provides transparent access to the trader’s performance, including detailed statistics that help assess both returns and associated risks. A robust track record can be a reliable indicator of a trader’s capability and stability.
How to avoid forex and CFD scams?
Unfortunately, the forex and CFD markets are rife with scams, but you can avoid them through diligent research. Utilizing resources like FX Empire, where experts and analysts share insights, can help you make informed decisions.
It’s crucial to choose brokers that are regulated within well-established jurisdictions. These brokers are more likely to offer a higher level of safety and transparency concerning your funds. Be wary of managed account providers that use unregulated, offshore brokers, as these often lack transparency and do not provide adequate security.
Another issue to be cautious of, which I’ve observed in the early stages of managed accounts and social trading, involves traders who restrict visibility of their current open positions. They may only reveal winning positions, thus presenting overly positive results while hiding open losing trades. Always ensure that you can view both open and closed trades before deciding to follow a trader or invest with them. This transparency is essential for a true assessment of their performance.